Arthrosis -In a disease that has many factors and is associated with degenerative-dystrophic damage to the joints. One of it is a violation of the metabolic processes in the body. The development of the disease through arthrosis is associated with blood disorders in the capillaries of the layers of the periosteum and as a result of this disorder of the nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the joint. At the same time, the structure of the cartilage itself changes and it becomes sharper, it becomes less elastic, the smoothness of the surface of the joint also decreases. Reducing the quality of cartilage tissues leads to a significant reduction in the volume of synovial fluid and deterioration of lubrication of the affected joint.
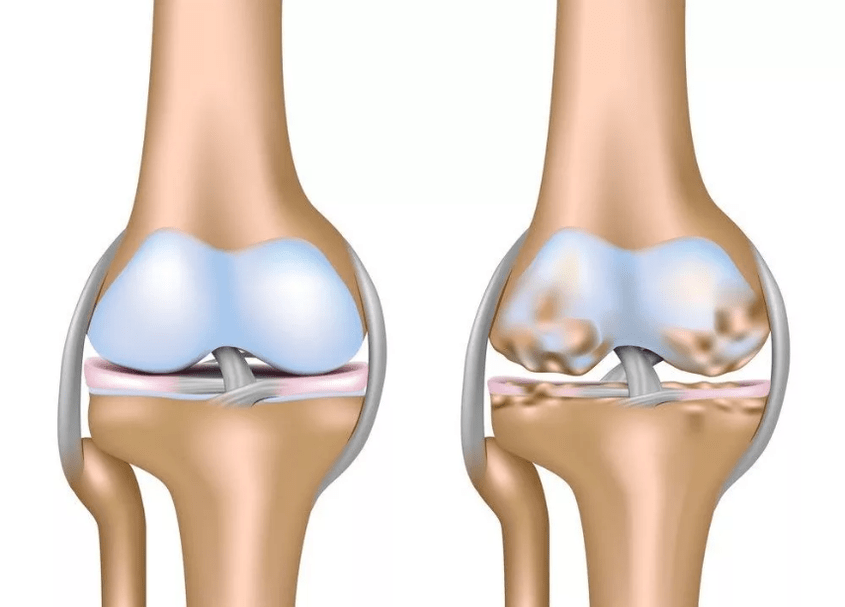
The folk name of the disease through arthrosis is "delayed salts", which is not true, since in the case of arthrosis disease the cartridge and capsules of the joints are destroyed, which leads to an increase in the load on the affected joint and as a result of the deformity of the bone. As a result, crispy, often accompanied by pain, appears in the joint, since osteophytes (bone spikes) are formed at the edges of the surface of the joint - hence the people's name of the disease through arthrosis.
Arthrosis, as a rule, mainly affects older people. Uncomfortable statistics show that more than 30% of people over sixty and about half, over seventy years, receive arthrosis.
Although this disease is based on the lesion of the cartilage of the joint, the process of the disease is also striking in the adjacent tissues - the synovial membrane, the periarticular muscles, the inner layers of the joint sac, bone structures and ligaments.
Symptoms of arthrosis
The arthrosis of the disease is symptomatic, first of all, the appearance of severe night pain during a change in the body or other movement. Pain, at rest with arthrosis, usually does not occur. One of the symptoms of arthrosis can be considered a characteristic crisis in the joints with pain. Also, arthrosis is often characterized by a very pronounced meteus sensitivity of patients - the manifestation of pain depending on the changes in time.
In general, arthrosis affects the hip and knee joints. A little less often - affects the joints of the fingers on the hands and feet, as well as the ankle. In the initial stage of the disease, the common symptoms of arthrosis are short -term and mild pain, which do not have clear localization and increase precisely during physical activity. Poor mobility of the joint is observed after a rest state and a feeling of increasing discomfort. With the development of arthritis, the clinical picture can worsen and over time the pain becomes more pronounced, the characteristic crunch of the joint becomes a permanent character, and the constantly more adultery pain leads to muscle spasm associated with the limitation of the amplitude of movements in the affected joint. In the short stages of arthrosis, with damage to the joints of the lower extremities, the limb appears and the patient should use crutches or cane.
Stages of arthrosis
In accordance with a classification based on radiological characteristics, four stages of arthrosis are distinguished:
- Grade I - Doubtful Arthrosis: The pain is almost not felt, manifests itself periodically and only at the beginning of the movement and quickly passes with its beginning. There is a slightly limited movement in the joint after a state of rest, quickly passing with the beginning of the movement. At the beginning of bending in the joint there is a pronounced crisis, but without pain, so that patients rarely come to a specialist for help.
- Grade II - Mecca Arthrosis: It is characterized by an increase in pain after high physical exertion -they become deeper and longer. Crustral tissues in the joint begin to lose their depreciation properties, osteophytes (bone spikes) are noticeable in the X -lies and the joint gap narrows. The patient can no longer do any work and his ability to work is reduced. At this stage, the patient is usually already looking for a doctor.
- Grade III - moderate arthrosis: It is characterized by its severity and neglect of arthrosis. Increasing the accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity and subsequent growth of bone tissue, resulting in deformation of the joint itself. The patient is tormented by pain even at rest due to the spasm of the near muscle joint while a decrease in the amplitude of the engine is observed. The lowest joint load causes the patient's suffering.
- Grade IV - severe arthrosis: It is characterized by a significant narrowing of the gap of joints, large osteophytes, as well as irreversible bone deformities. The patient can no longer move and only the implantation of the artificial joint prosthesis can help to avoid disability through surgery.
The causes of arthrosis
Arthrosis is a consequence of the impaired function of cartilage tissue due to changes in its structure. The cartilage of the joint is softened and loosened while in the joint that wears the load, ulcers begin to form.
The onset of the disease through arthrosis is divided into two methods:
- Primal Arthrosis (idiopathic) occurs for no apparent reasons. They can be like hereditary factors: genetic disorders in cartilage, congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system, and others, in some way: hypermiors of the joints, flat legs, etc.
- Secondary Arthrosis is caused by the development of pathological processes: congenital joint disorders, injuries, metabolic disorders, a number of endocrine diseases, specific and non -specific and specific inflammation.
Arthrosis
Effective treatment of arthrosis is only possible overall and should be performed after consultation with a specialist. The main stages of arthrosis treatment include:
- Anesthesia by taking analgesics.
- Removal of inflammation with anti -inflammatory drugs.
- The restoration of cartilage tissue of the joint with the help of medicines containing in their composition of medicines selected individually by the course for several months.
In combination with these three stages, physiotrosis is an integral part of the treatment of arthrosis - magnetotherapy for arthrosis, electrophoresis, acupuncture, and massage. At the same time, it is not unimportant to adhere to a properly selected diet.
Prevention of arthrosis
In order to prevent arthrosis, it is necessary to minimize the static load of the joints. The constant wearing of high mill shoes should be avoided. It is not recommended to sit in the position of "feet placing your feet". More often, sitting and straightening provisions must be alternated. If there is excess weight, then you should get rid of it. The best diet to prevent arthrosis is food for foods with predominance of carbohydrates, vegetables, fruits, limiting the intake of proteins and calcium. Try to avoid weight lifting. In the summer, organize a "vacation" of your joints - swim as much as possible!



































