Osteochondrosis is a pathology in which the intervertebral discs that separate the vertebrae are destroyed. Degenerative-dystrophic tissue changes can develop at different speeds and manifest with different symptoms. The clinical picture depends on which part is affected and what caused the disease.
Main characteristics
Destructive processes in the spine can lead to irreversible consequences that significantly complicate a person's life. They can affect any area - cervical, thoracic or lumbar - or spread throughout the spine.
In most cases, osteochondrosis occurs in waves: periods of exacerbation alternate with periods of remission. In this case, 3 variants of the flow are possible, different in nature:
- progressive - each subsequent exacerbation is accompanied by more severe symptoms, the intervals between them are reduced;
- regression - the frequency and intensity of attacks constantly decreases;
- stable - exacerbations occur regularly with the same symptoms.
It is also worth noting that damage to different parts of the spine not only manifests itself differently. The therapeutic approach and treatment methods also have their own characteristics.
Stages
Pathological changes in the discs and vertebrae do not appear immediately. Their development is preceded by deterioration of blood circulation and nutrition of the paravertebral (paravertebral) structures caused by external and internal factors.
Degeneration of osteochondral tissue occurs in all people with age and serves as one of the signs of aging of the body. However, this process can be dramatically accelerated after an injury or as a result of a general illness.
The early appearance of chondrosis is greatly facilitated by overloading the back - both dynamic and static, when a person is forced to stay in the same position for a long time.
Cervical osteochondrosis occurs in 3 stages, each of which is characterized by its own manifestations:
- Stage 1. Headaches and discomfort in the back of the neck and the back of the head periodically appear;
- Stage 2. The headache becomes more frequent, sometimes you feel dizzy and the ability to work decreases. At stage 2, patients most often consult a doctor, but it is no longer possible to achieve a complete recovery of the damaged structures;
- Stage 3, final. It is characterized by extensive damage to the vertebrae, discs and ligamentous system. It manifests itself as a severe and almost constant headache, loss of coordination of movements, stiffness in the cervical vertebrae, as well as reduced vision and hearing.
Some experts distinguish 4 stages of osteochondrosis: the last one is accompanied by almost complete loss of mobility and severe neurological symptoms.
From stage to stage, the pulpy core of the disc loses moisture, and with it the elasticity disappears, and the shock-absorbing qualities decrease. The intervertebral disc dries out, flattens and cracks. Adjacent vertebrae move closer to each other, which in turn provokes displacement of the facet joints. All this leads to pinching of the spinal nerves, pain and other symptoms.
IMPORTANT: the therapy of stages 2 and 3 of osteochondrosis comes down to preventing relapses and maximizing the remission phase.
Causes of exacerbation
In order for cervical chondrosis to worsen, exposure to one or more factors is necessary, among which doctors call:
- high loads on the back and spine associated with lifting heavy weights or changing the training program for athletes;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- massage or manual therapy procedures performed by an unqualified specialist;
- seasonality - exacerbations most often occur in spring and autumn;
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy and menopause;
- the presence of chronic diseases that weaken the body, including frequent colds;
- sudden weight gain.
Symptoms
An attack of cervical osteochondrosis can begin with the appearance of discomfort in the shoulder girdle and occipital region. At the same time, the general well-being deteriorates, a person quickly gets tired and copes with professional and daily duties worse.
Sometimes there is a sudden exacerbation with a severe headache. Often (in 72% of cases) certain signs indicate the approach of an attack - in particular, a feeling of heaviness in the head, dull pain in the neck and shoulder girdle. Symptoms are usually worse in the morning.
Symptoms of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis have significant similarities with the general clinical picture of this disease. The main symptom is pain of varying intensity and character. The back of the neck on one or both sides and the head may hurt. Often the pain spreads to the collarbone and shoulders. In some people, painful sensations occur only when turning or tilting the head or when moving the arm.
IMPORTANT: sometimes cervical chondrosis "masks" as a heart attack and causes pain behind the sternum, under the shoulder blade and in the left arm.
Signs of acute osteochondrosis may also include:
- vertigo;
- worsening of sleep, decreased concentration, memory problems;
- flickering of spots before the eyes, noise and ringing in the ears;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- diction disorder;
- disturbance of sensitivity of the neck and hand.
There are no "painless" variants of the course of osteochondrosis, damage to any of the departments is manifested by pain of different localization and intensity
Cervical chondrosis cannot be ignored, it must be treated. Without treatment, it will not only worsen more often, but can also cause a serious complication in the form of a stroke. The cause of an acute cerebrovascular accident is compression of large arteries supplying the brain.
How long does the exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis last?
The duration of the attack depends on the factor that provoked it, the season and the general state of health of the person, as well as on the methods of treatment. Exacerbation is more difficult to tolerate and lasts longer during the cold season.
On average, the acute period lasts from 4 days to a week, after which the pain gradually decreases, which takes about another three weeks. The total duration of the exacerbation is a month and a half.
What to do
The best thing you can do if you suspect cervical chondrosis is to visit a neurologist or orthopedist. He will prescribe the necessary tests, find out what leads to exacerbations and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Before visiting a doctor, you should avoid straining your back and take the most comfortable position. It is recommended to lie on a flat and elastic surface to maximally relax the neck muscles and reduce the intensity of the pain. It is recommended to isolate the sore spot with a scarf, handkerchief or wrap yourself in a blanket.
It is very important to immobilize the cervical spine and try not to rotate or tilt your head too much. For this purpose, doctors even advise wearing special orthopedic collars. You can make them yourself from cotton wool and cardboard or buy them at the pharmacy.
IMPORTANT: the orthopedic collar is worn no more than four hours a day, otherwise it will cause harm, not benefit, and recovery will be delayed.
The most famous of the neck braces is the Shantz collar. It is an indispensable tool for temporary unloading and stretching of the spine in the cervical region. Despite its rather rough appearance, such a splint, when correctly selected, provides comfort and significantly reduces pain.
Severe pain is relieved with painkillers. The most effective are drugs from the group of NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In case of exacerbation of osteochondrosis, it is forbidden to warm the affected area in any way - with a heating ointment, applying mustard or compresses, a steam bath in a sauna. Do not massage the affected area or self-medicate.
Treatment
The treatment of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis is carried out with medicinal and non-medicinal methods. The latter include physiotherapy, massage and gymnastics. Traditional medicine can have a good effect, provided it is agreed with the attending physician.
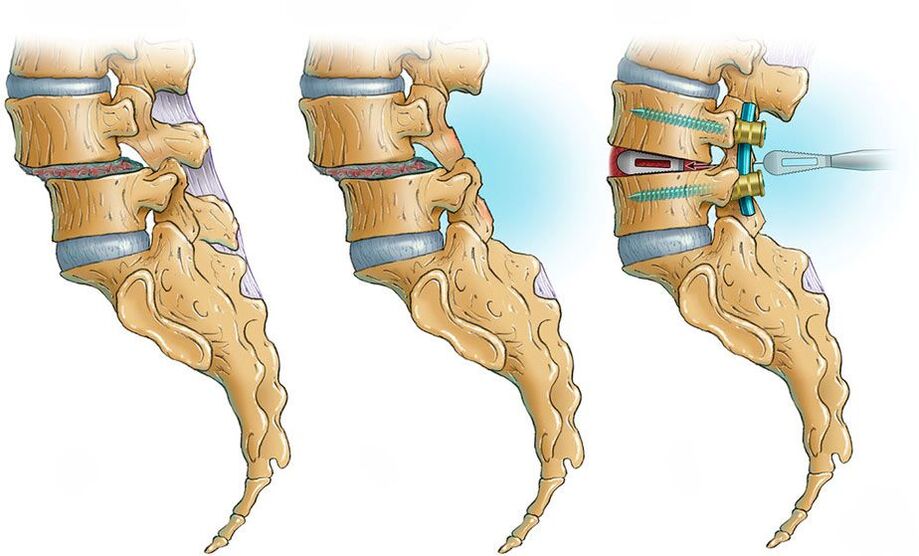
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis is performed only in extreme cases and consists of partial or complete removal of hernia, osteophytes (bone growths)
In the acute period, the main efforts are aimed at relieving pain. Depending on its intensity, analgesics and NSAIDs are prescribed in the form of injections or tablets. These can be drugs based on the substances diclofenac, ibuprofen, nimesulide, metamizole sodium. In addition to them, the use of anti-inflammatory ointments is recommended.
Muscle relaxants will help relieve muscle spasms. If there is swelling, then diuretics are prescribed, which remove excess fluid, thereby reducing the pressure on the nerve endings.
After elimination of acute symptoms, vitamin complexes containing vitamins of group B are added to the treatment; nootropics that normalize the transmission of impulses along nerve fibers; chondroprotectors to restore and strengthen the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy, which can be prescribed in the subacute phase and continue during the remission period, helps to quickly relieve the exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis. They help to improve the blood supply to the injured segment, relax the muscles and reduce pain and inflammation. The most effective methods are traditionally considered to be electrophoresis, ultrasound, magnetic and cryotherapy (treatment with cold).
At the beginning of the remission period, massage sessions are prescribed, which can be performed both in a specialized office and at home. It is best to practice both.
Medical therapy
If chondrosis of the cervical spine has worsened and is accompanied by severe pain, the person is prescribed strict bed rest. As the pain subsides, one switches first to semi-bed rest, and then to gentle motor mode.
It is useful for all patients with any stage of chondrosis to sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow. Such accessories maintain the anatomically correct position of the body and relieve stiffness and pain in the morning due to a slight pull on the spine. In hospitals, a Glisson loop is used for this purpose.
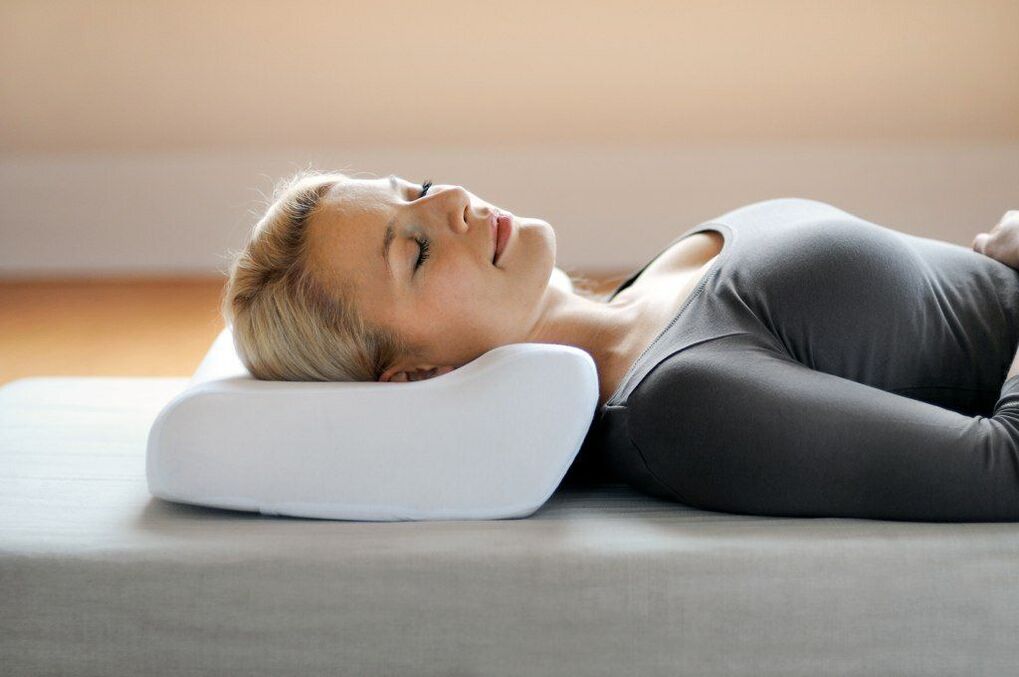

The preferred positions for cervical chondrosis are on the side and on the back. An important condition is a comfortable and "correct" pillow, preferably orthopedic.
When the acute pain passes, they begin physical therapy exercises. In combination with other methods, its effectiveness is very high. The first workouts should be conducted under the supervision of an instructor who will select and teach you how to perform the exercises correctly.
IMPORTANT: the tempo and amplitude should be increased gradually, expanding the program and increasing the load over time.
Gymnastics according to Bonina
- While sitting or standing, raise your arms up. With an inhale, connect your fingers at the top and lower your clenched hands down. The neck stays in place.
- Half shoulder rotation. Pull your shoulders back in an arc in the air and bring them back in the same arc.
- Stretch your head forward and stay in this position for a few seconds.
- Turn your head now to the right, now to the left, looking over your shoulder each time.
- Simultaneously raise the right shoulder and lower the left shoulder.
Gymnastics according to Bubnovsky
- Sitting in a chair, turn your head to the right and lower your chin to your shoulder, stay in this position. Then repeat the exercise to the left side.
- Tilt your head toward your chest while gently pulling your neck forward and up.
- Turn your head with the chin up, first to the right, then to the left. Then repeat the exercise by raising your arms up and closing your fingers.
- Place your left hand on your right shoulder and turn your head to the left. Hold for a few seconds and turn your head to the right, placing your right hand on your left shoulder.
- Place your hands on your hips and slowly stand up, moving your back back and pulling your neck up.
- Starting position - standing, head down. Move your chin smoothly first to the right and then to the left shoulder, dropping it each time at the midpoint towards the chest.
Traditional methods
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home includes water and warming procedures and the use of orthopedic devices. Lotions and compresses made from vegetables and herbs are always in demand and popular.
In case of exacerbation, you can take a warm shower and wrap your neck with a warm scarf. To reduce pain and inflammation, lotions are made from herbs - for example, sage and peppermint. To prepare a healing solution, brew one or two tablespoons of the herb in a glass of boiling water and leave for 15-20 minutes. After it cools down to a comfortable temperature, wet a cotton pad or bandage and apply it to the area where it hurts for 10-20 minutes. The procedure is performed up to 4 times a day.
Onion compress is prepared from grated or pureed onion in a blender. The resulting mass is distributed on gauze and applied to the neck, covering from above with food film and cotton cloth. After 2-3 hours, the compress is removed and the skin is washed with warm water.

Therapeutic compresses are a simple, affordable and very effective method of treatment if used correctly.
The application with kerosene is done as follows: a linen or cotton cloth (you can use gauze or a bandage) is dipped in kerosene and applied to the neck area. Cover the compress on top with cotton wool or polyethylene so that it does not spread. Leave for no more than three hours, if a strong burning sensation occurs, immediately remove and rinse with water.
A product with the following composition is used as an ambulance for acute chondrosis of the cervical vertebrae:
- 5 tablets of analgin, ground into powder;
- ethyl alcohol - 15 ml;
- camphor alcohol - 5 ml;
- iodine - 5 ml.
Mix everything and rub into the skin over the sore spot.
Osteochondrosis can also be treated "from the inside" by taking, for example, an infusion of pine buds. In this recipe, ready-made from the pharmacy or fresh ones picked in early spring are used. Fresh buds must be pre-cut.
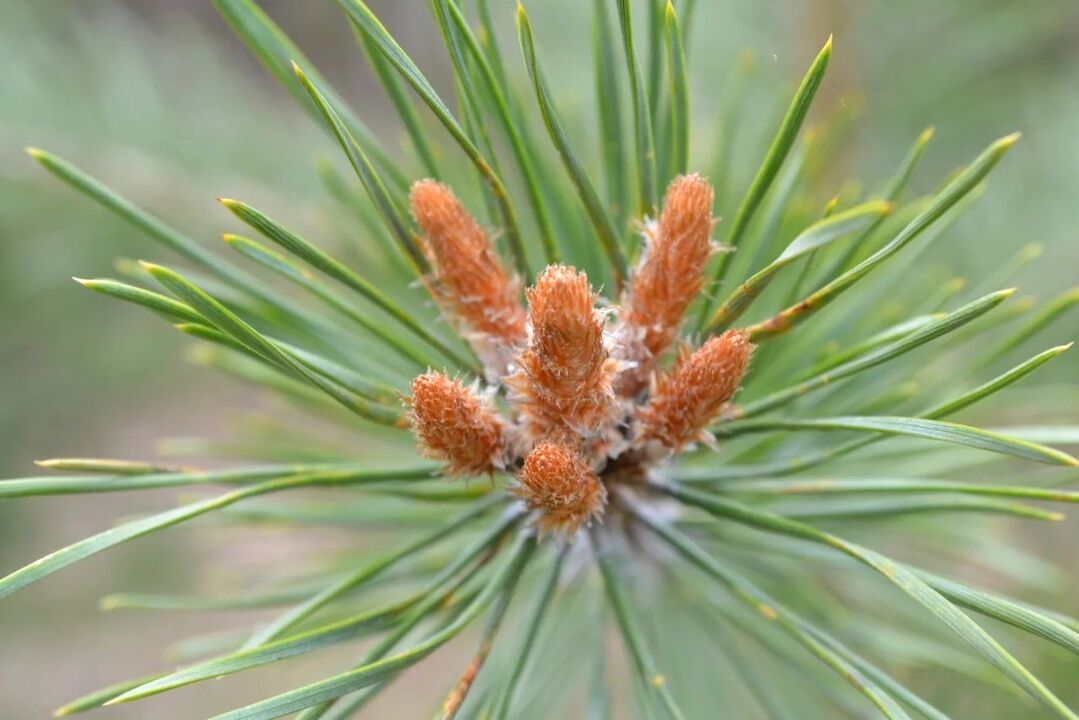

For medical purposes, it is better to use buds of medium size, as they contain more useful substances.
The raw materials are covered with sugar in a 1: 2 ratio and infused for two weeks. Use the finished product one teaspoon three times a day. To enhance the effect, you need to keep it in your mouth for a while and only then swallow it. The course of treatment is up to three weeks.
Things to keep in mind
All doctors insist that the early stages of osteochondrosis go almost unnoticed and are not particularly disturbing. At this stage, when the symptoms are limited to only mild discomfort and mild stiffness in the morning, you can only heal with the help of exercise therapy. No medication will be needed, but you will need to adjust your diet and lifestyle.
The best prevention of both the disease itself and its relapses is physical activity. Regular physical exercises will maintain good posture and help prevent the development of destructive processes in the spine.
In severe, advanced cases, much can also be done. The systematic application of therapeutic gymnastics complexes and a course of drug treatment will significantly improve well-being and reduce the risk of new exacerbations.
FAQ
What symptoms of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis can occur?
During an exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, the patient may feel pain in the neck, shoulders, arms, dizziness, a feeling of numbness or tingling in the hands, as well as limited mobility of the neck.
What factors can provoke an exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis?
Exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis can be caused by overloading the neck, prolonged stay in the wrong position, trauma, stress, as well as age-related changes in the spine.
What methods of treatment of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis can be effective?
Non-drug methods (massage, physiotherapy, exercises), drug therapy and, in some cases, surgical intervention can be used to alleviate the symptoms of an exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis.
Useful tips
Tip #1
Maintain proper posture and avoid standing in an incorrect position for long periods of time. Do regular neck and back exercises to strengthen your muscles and improve flexibility.
Tip #2
Avoid sitting in front of a computer or monitor for long periods of time. Take regular breaks to stretch your neck and back, do eye exercises and exercises to relax your neck and shoulders.
Tip #3
Use a pillow and mattress that support the correct position of your neck and back while you sleep. This will help reduce the load on the spine and prevent exacerbation of osteochondrosis.



































